Introduction
You might download a picture and you see the words .JPG, .PNG, .GIF, .TIFF, etc at the end of the file. And it is highly possible that you cannot figure out what they stand for.
Well, these are file formats. We often come upon the four file formats TIFF, PNG, GIF, and JPG. So, you might think- Which is the best of all of these formats? You may also ponder- When should we use JPG, PNG, and GIF? What are TIFF images? Where do we use them, are they even different? What of we use the wrong image format in the wrong place?
Our article will help you understand the differences between these four formats. You will find every single detail you need to know about JPG, TIFF, GIF, and PNG down below. We have designed this article to answer all of these queries. By the end of this article, you’ll know about the uses of different image file formats and when to use which file type.
What is a file format?
The file type or format refers to a file’s structure, which instructs a programme on how to display its contents. A Microsoft Word document, for example, saved in the word file extensions .doc or .docx.
Microsoft Word is the finest programme for viewing DOC files. Even if another application can open the file, it might not have all of the necessary functionality to display it appropriately.
Before we begin discussing about the various image formats, let’s clear our basics. What is an image file format exactly? Let’s get to that now.
![]()
Image file format- what does that mean?
Image file formats are a set of standards for organising and storing digital photographs. Uncompressed data, compressed data (which can be lossless or lossy), or vector data can all be stored in an image file format. Image files are made up of digital data that has been rasterized for usage on a computer display or printer in one of these formats.
Various image file formats available
No one can keep track of the vast variety of image file types available in this era of technology, not even the most experienced developers. Using the incorrect (or poor) file format can lead to many distinct issues.
It could lead to poor quality of images, unnecessarily huge file sizes, the process of sending these large files can become very slow, data may become inaccessible within the filer.
In simple terms, it’s critical to recognise and comprehend the various types accessible, as well as their functions, features, and capabilities. But where do we begin with so many different file types?
A few very popular image file formats:
- JPG/JPEG
- GIF
- TIFF
- PNG
- PSD
- BMP
- WEBP
- RAW
- HEIF
- INDD
- JPEG 2000
- EPS
- AI
- SVG
In this article, we’ll mainly focus on PNG, JPEG, GIF, and TIFF image file formats. So, let us begin.
PNG
Portable Network Graphics is the full name for PNG file formats. PNG is a free and open-source alternative to GIF. It has a colour palette of 16 million. For true-color photographs that require excellent tone balance, this is the optimal file format.
![]()
The APNG format can be used to create animated PNG files. The background of these files is translucent. Raster images of 8-, 24-, or 48-bit resolution. True colour PNGs have a bit depth of 24 or 48 bits and can store over 16 million colours.
Uses: PNGs are typically used for high-resolution, colourful photos and photographs. They are similar to JPGs but there are a lot of differences as well. We’ll address those in the further sections.
JPEG
Joint Photographic Experts Group is the full name of the file format JPEG. It is considered as the most prevalent image file format used by digital cameras to save images.
JPEG files use the lossy compression approach, which can greatly reduce file size without sacrificing quality. Microsoft Paint files are saved in this format by default. JPEG files are raster images with a 24-bit colour depth and excellent resolution.
![]()
Uses: These are used for realistic picture quality. Also, for intricate graphics with vibrant colours, this is the best option. JPGs employ lossy compression, which results in a smaller file size. Lossy compression, on the other hand, leads in a reduction in image quality after each image alteration.
GIF
Graphics Interchange Format is its full form. It is the most prevalent image animation format, despite having a lower compression ratio than most video formats.
Only an 8-bit palette (256 colours) is available. This makes it unsuitable for photographic pictures or dithering. GIFs, like PNGs, can render transparent images.
![]()
Uses: The GIF file format can only hold a limited number of colours. So, it is considered as perfect for making simple graphics and logos. Animated GIFs are also possible to create. Hence, GIFs are mostly used for animations.
TIFF
TIFF stands for Tagged Picture File Format. It is a raster image format. TIFF is most commonly used in publishing.
These files are huge but lossless. That is what makes them ideal for photographs that are often modified. They can hold tags, layers, and transparency when utilised with a programme like Photoshop. But this format is not suggested if you are seeking for a compact or web-compatible file.
Uses: TIFFs are appropriate for cases when you don’t want to sacrifice image quality but don’t care about file size. If you’re storing photos to print later, that could be one of the situations. If you’re using desktop publishing software, you could need them, or they’re what your scanner sends to your computer.
The basic differences between them
The debate over whether JPG, GIF, PNG, or TIFF is better for the web has been going on for quite a long time now. But there is no right or wrong answer in this case, for sure. The best thing we can do, is make an informed decision that will better serve our needs.
A few of the basic differences between each of these image file formats are as follows.
- PNG files, unlike JPGs, allow transparency. Hence, we can say that, the objects in an image can be made transparent. PNGs are also lossless, which means that no matter how many times a picture is modified, the quality will remain the same.
- But the same is not true for JPGs. The JPEG format is not at all resistant to degradation over time. This means that the image quality will deteriorate with each modification and resave.
- The PNG file format works best with files that are larger in size. But it is important to keep in mind that animated visuals are not supported by the PNG format. GIF format supports animations instead.
- But at the same time, GIFS have low compression ratio than most of the video formats that are available. And also, the colour palette for is limited to 8 bits (256 colours), unlike PNG and JPG, making it unsuitable for photographic pictures or dithering. PNGs support 8, 24, and 48-bit images, while JPG supports 24-bit images.
- Now, TIFF file format supports transparency just like PNG. This makes it different from JPEG. They are also lossless, and hence, the quality is not degraded after any sort of modification.
- But, while JPGs can be used in cases where smaller sizes are required, PNG and TIFF cannot. Also, TIFF files are absolutely not appropriate for web browsers. If we need images for the web, we can use PNG files, as PNG files are web- friendly.
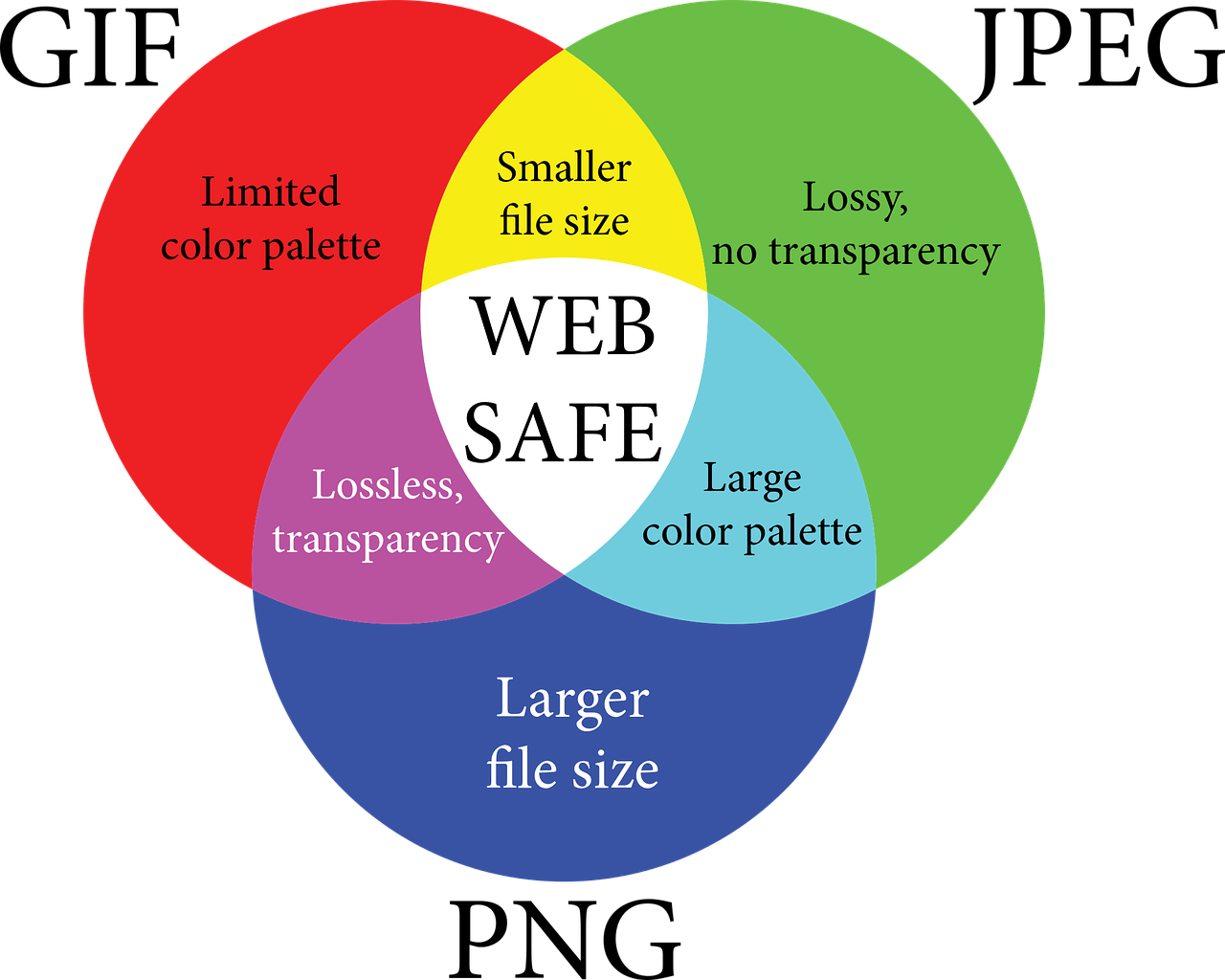
These are the very basic differences between these four formats. The list of formats definitely does not end here. But, in this article, we’ve tried to cover these fundamental file formats that you’ll definitely come across more frequently.
Conclusion
We hope that our article succeeded in providing the fundamental idea of the image file extensions JPG, PNG, GIF and TIFF. Hopefully, with this guide, you now know the differences between these file formats, and have developed a basic idea regarding when to use which.
Either way, we would advise that you choose whichever format fulfills your requirements in a better and efficient manner.

In case you come across formats other than the ones we’ve mentioned here, you can check out our File Type Checker tool and find out, in detail, about the type of file you are using. After that you could conduct a little more research on that format in your preferred search engine, and henceforth, make informed decisions.






